Overview
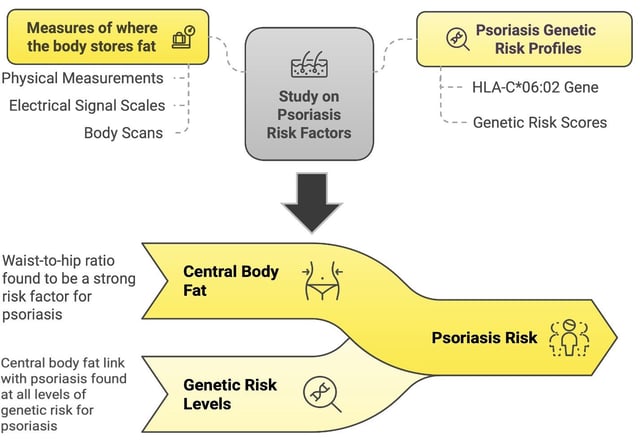
- A UK Biobank analysis of over 330,000 participants, including more than 9,000 with psoriasis, found waist-to-hip ratio to be the strongest predictor of disease risk regardless of genetic factors.
- Study authors recommend incorporating waist circumference measurements and proactive weight-management strategies into psoriasis risk assessment and care.
- Abdominal adipose tissue is believed to promote psoriasis through inflammatory cytokines and disrupted hormone signals, prompting deeper investigation into underlying mechanisms.
- Dermatology experts are calling for large-scale clinical trials of GLP-1 receptor agonists—currently used for diabetes and obesity—to evaluate their impact on psoriatic inflammation.
- The findings highlight the interplay between central obesity, chronic inflammation and skin health, guiding future personalized prevention and treatment approaches.