Overview
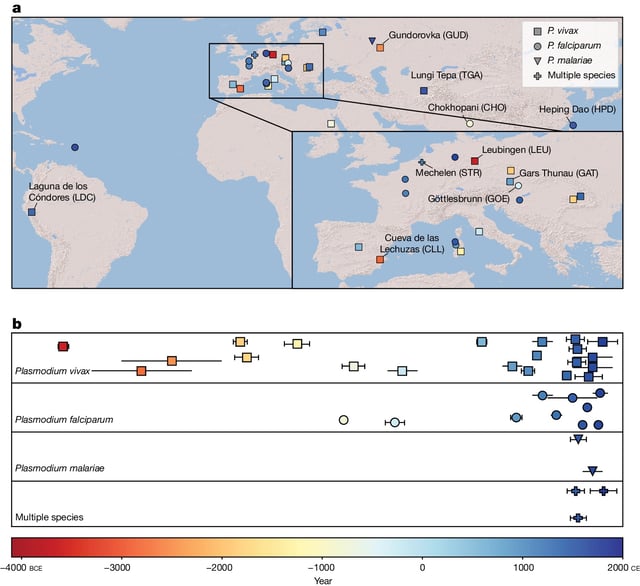
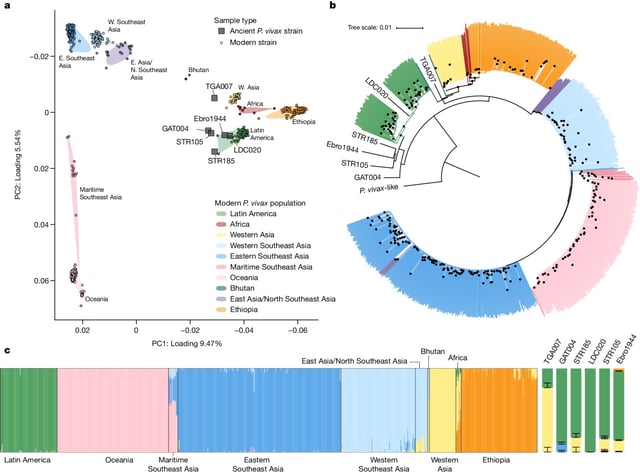
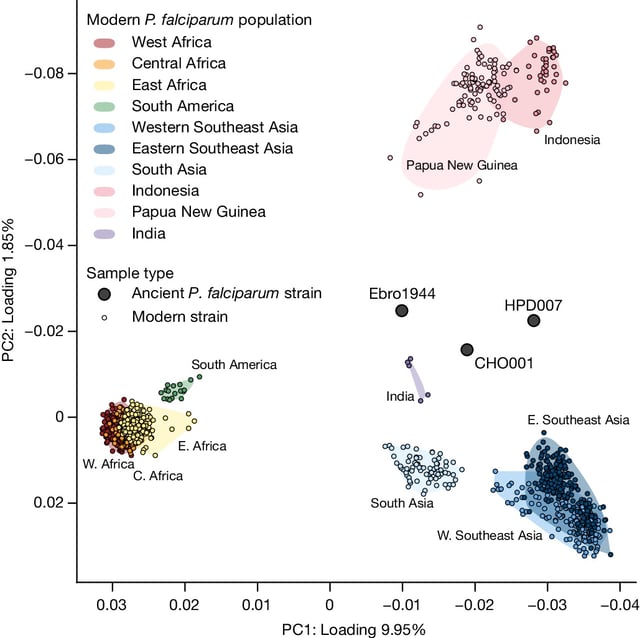
- Scientists reconstructed genomes from 36 malaria-infected individuals spanning five continents and 5,500 years.
- The study identifies trade, warfare, and colonialism as key factors in the spread of malaria.
- Evidence shows malaria reached the Americas through European colonizers within the first century of contact.
- Unexpected findings include a high-altitude malaria case in Nepal, likely contracted through trade routes.
- The research highlights parallels between ancient and modern disease spread due to human mobility.