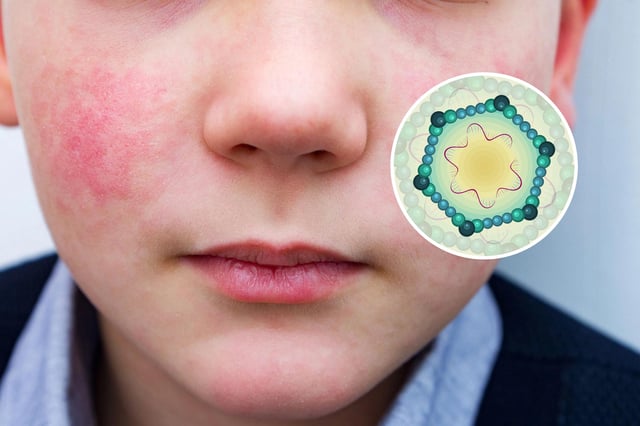
Overview
- Parvovirus B19 cases have surged, particularly affecting children aged 5 to 9.
- The virus can cause severe complications in pregnant individuals, including fetal anemia and miscarriage.
- People with blood disorders or weakened immune systems are at higher risk of serious illness.
- There is no vaccine for parvovirus B19; prevention relies on hygiene and respiratory precautions.
- The CDC urges awareness and vigilance among healthcare providers and the public.