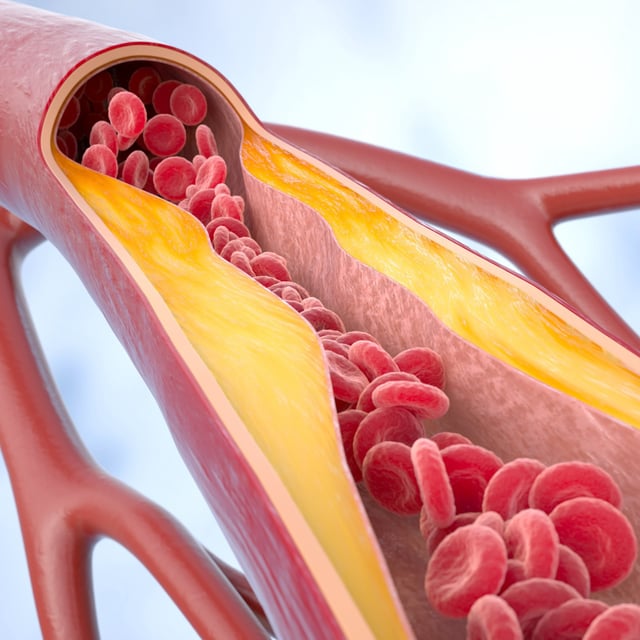
Overview
- Scientists found that fluctuating cholesterol levels in early life significantly increase the risk of atherosclerosis.
- The study suggests that intermittent high-fat diets are particularly harmful in terms of developing arterial plaque.
- Researchers used both mouse models and long-term human data to support their findings.
- High cholesterol exposure in childhood is linked to greater plaque buildup in arteries by middle age.
- Health experts emphasize the need for early cholesterol monitoring and lifestyle changes to prevent heart disease.