Overview
- Firefly Aerospace's Blue Ghost lander successfully landed upright on the Moon's Mare Crisium on March 2, 2025, as part of NASA's Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative.
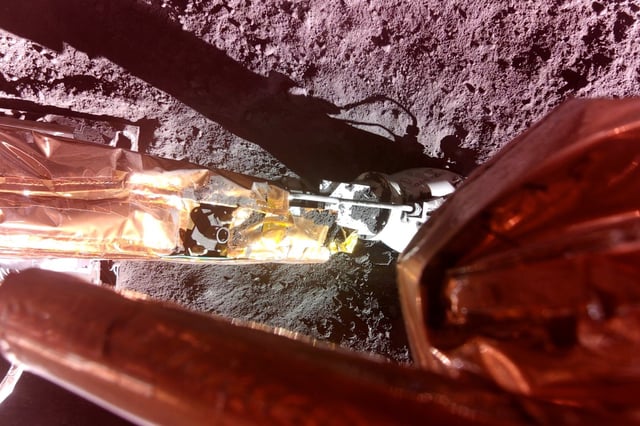
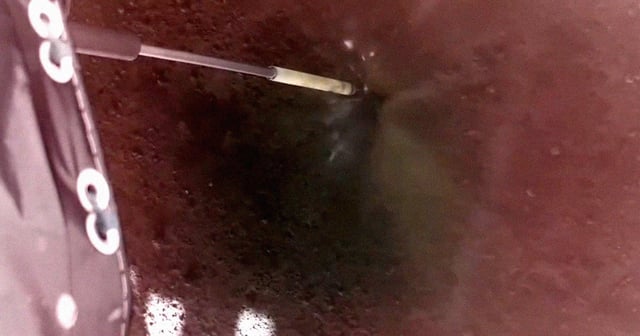
- The lander is conducting the Lunar Instrumentation for Subsurface Thermal Exploration with Rapidity (LISTER) experiment, marking the first robotic collection of lunar heat-flow data since the Apollo missions.
- LISTER's pneumatic drill, developed by Texas Tech University and Honeybee Robotics, is designed to measure thermal conductivity and heat flow by drilling nearly 10 feet into the lunar surface.
- The mission aims to provide insights into the Moon's geological evolution and support the development of sustainable human exploration under NASA's Artemis program.
- Blue Ghost carries 10 NASA payloads, including experiments on lunar dust mitigation and regolith adhesion, and is expected to operate for a full lunar day (14 Earth days).