Overview
- Researchers from Japan conducted genome-wide DNA methylation analysis on postmortem brain samples from individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and neurotypical controls.
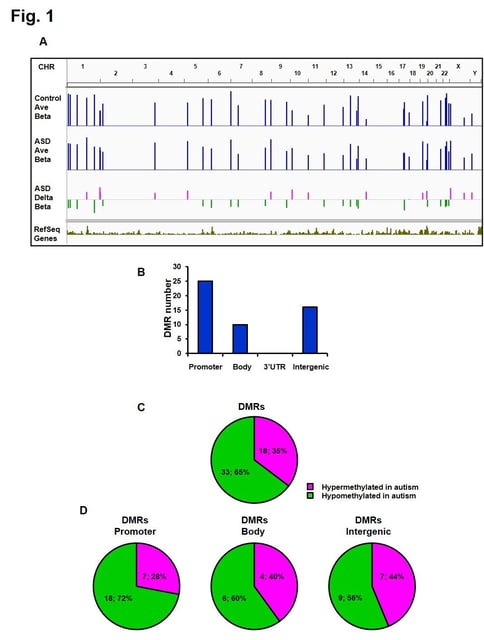
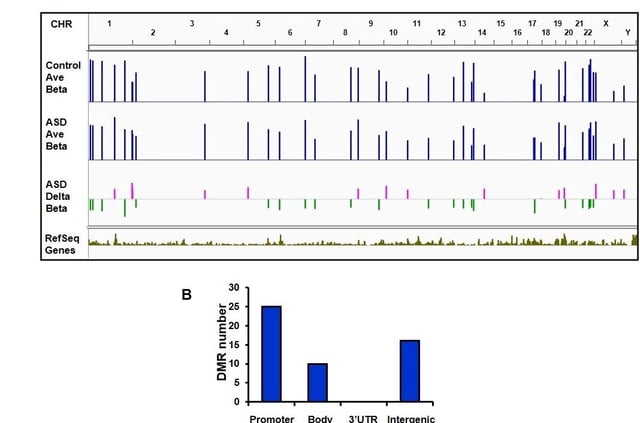
- The study identified hypermethylation of OR2C3 and HTR2C, genes tied to sensory processing and serotonin signaling, in ASD brain samples.
- A previously unrecognized gene, RABGGTB, exhibited hypomethylation and increased expression, highlighting its potential role in neuronal health and autism pathology.
- RABGGTB is absent from existing autism gene databases, such as SFARI, positioning it as a novel candidate for further research into ASD etiology and biomarkers.
- The findings emphasize the need for integrated transcriptomic studies and in vivo models to validate these epigenetic insights and explore their diagnostic and therapeutic potential.