Overview
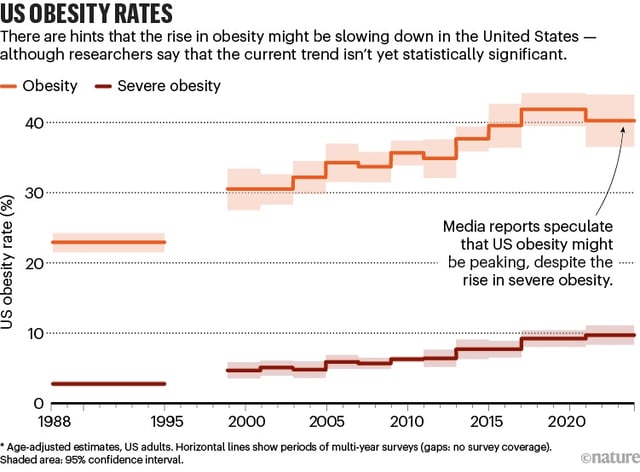
- GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as Wegovy and Ozempic, have surged in popularity, with usage in the U.S. rising from 190,000 to 1.8 million monthly claims since 2014.
- The drugs show promise in reducing obesity-related conditions but are accompanied by side effects and high costs, with prices exceeding $1,000 monthly for uninsured patients.
- Medicaid coverage for GLP-1 drugs is limited to 13 states, with others citing cost as a barrier despite potential long-term savings from reduced chronic disease rates.
- Demographic disparities are evident, as wealthier and white individuals are more likely to access these drugs, while minorities and lower-income groups face greater barriers.
- Analysts predict significant societal impacts from widespread GLP-1 use, including reduced obesity rates, economic benefits, and challenges for industries like food and transportation.