Overview
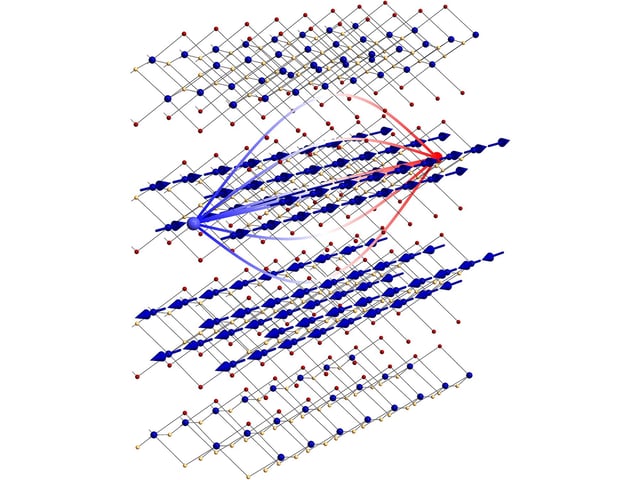
- Chromium sulfide bromide (CrSBr), a layered magnetic semiconductor, confines excitons to a single dimension due to its unique antiferromagnetic structure at low temperatures.
- Excitons, quasiparticles formed by electron-hole pairs, are stabilized and confined in CrSBr without the need for traditional 2D exfoliation techniques.
- The material's magnetic order allows excitons to retain quantum properties in bulk 3D structures, addressing a key challenge in scaling quantum technologies.
- This breakthrough could lead to applications in quantum computing, sensing, and advanced optical systems by leveraging CrSBr's ability to encode and transfer information using photons, spins, and vibrations.
- Collaborative research teams used optical spectroscopy and theoretical modeling to confirm the magnetic confinement's consistency across layers and its potential for quantum information processing.