Overview
- Scientists have found evidence that microquasars, small black holes that feed on stars, could be responsible for high-energy cosmic rays bombarding Earth.
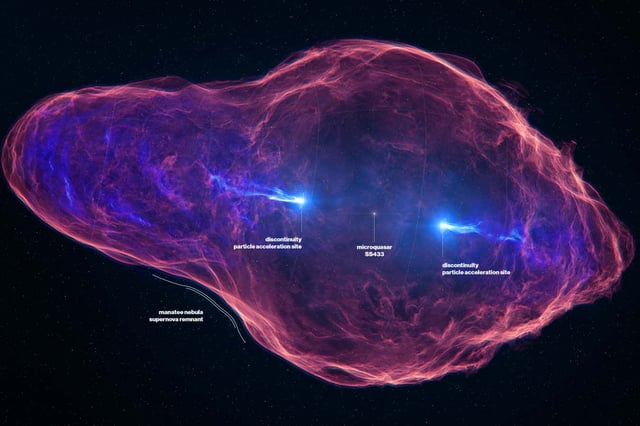
- The most powerful microquasar in the Milky Way, SS 433, was observed emitting extremely high-energy gamma rays, indicating that it could accelerate particles to the high energies observed in cosmic rays.
- SS 433, located in the Manatee Nebula, consists of a black hole and a supergiant star, with the black hole stripping material from the star and blasting it out at high speeds.
- Observations showed that the jets of material ejected from SS 433 reemerge in high-energy X-ray light around 75 light-years from the microquasar's origin, suggesting that something within each jet is accelerating particles to even higher energies.
- Despite these findings, SS 433 cannot be the source of the very high-energy cosmic rays detected on Earth due to its age, but other, older microquasars could be contributing to these cosmic rays.