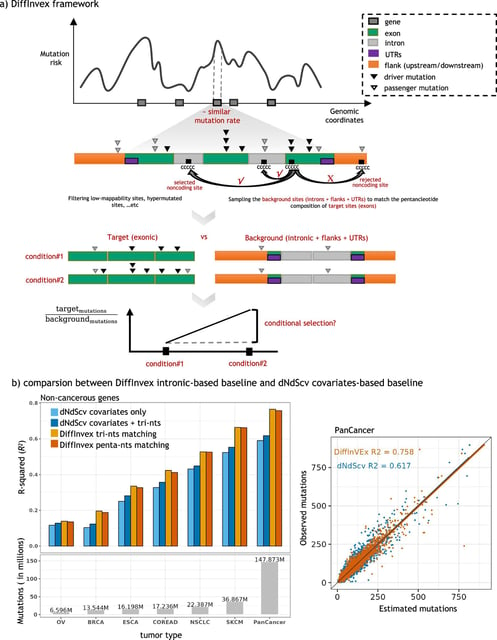
Overview
- The DiffInvex computational tool tracks how evolutionary pressures on genes shift as cells transition from healthy to cancerous and respond to chemotherapy.
- Analysis of over 11,000 genomes identified 11 genes, including PIK3CA and STK11, whose mutations are strongly selected after chemotherapy exposure.
- The study found that resistance arises from additional driver mutations in core cancer genes, not specialized drug-resistance mutations.
- ARID1A, long considered a cancer driver, was shown to accumulate mutations during normal aging, challenging its role in initiating malignancy.
- Researchers propose combining chemotherapy with inhibitors targeting core survival pathways to delay or prevent tumor relapse.