Overview
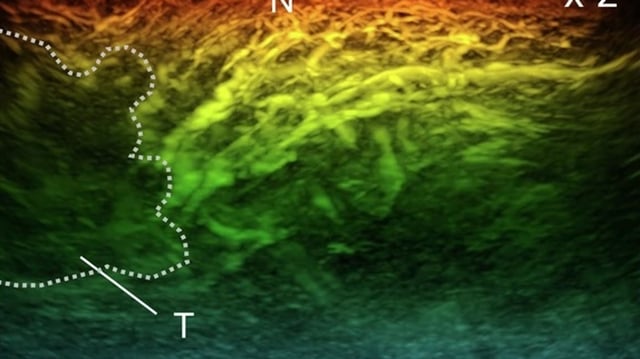
- The scanner uses Photoacoustic Tomography (PAT) to generate highly detailed images in seconds, avoiding motion blur.
- It provides a safer alternative to traditional imaging techniques like X-rays and MRI scans by using laser light and ultrasound waves.
- In trials, the scanner revealed important blood flow issues in early-stage diabetes patients, aiding in better disease management.
- The technology holds potential for early detection and treatment of cancer by visualizing abnormal blood flow patterns around tumors.
- Researchers aim to further refine the scanner's capabilities and test it on larger patient groups before clinical adoption.