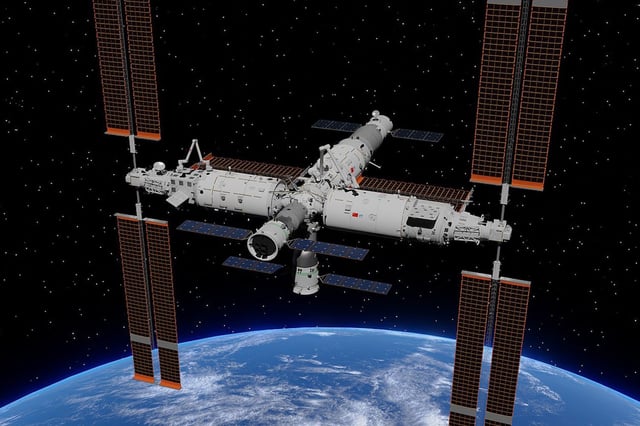
Overview
- Niallia tiangongensis, a newly identified bacterial strain, was discovered aboard the Tiangong space station and confirmed as genetically distinct from its Earth relatives.
- The microbe demonstrates enhanced resistance to radiation and oxidative stress, traits critical for survival in the harsh conditions of space.
- Astronauts on the Shenzhou-15 mission collected the microbial samples in May 2023 as part of China's CHAMP initiative to monitor space station microbiomes.
- Researchers are investigating whether the strain evolved in orbit or arrived pre-adapted, as well as its potential health implications for astronauts.
- The findings, published in the International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, contribute to understanding microbial evolution in space and inform biosecurity protocols for long-term missions.