Overview
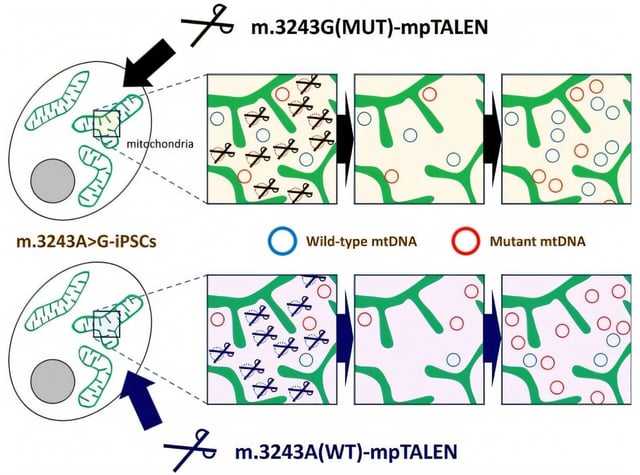
- Researchers from Japan have developed mpTALENs, a gene-editing tool capable of precisely altering the ratio of mutant to normal mitochondrial DNA in patient-derived stem cells.
- The platform allows bidirectional control of heteroplasmy levels, achieving mutation loads from 11% to 97% while preserving stem cell pluripotency and differentiation potential.
- Key innovations, including novel DNA-binding domains and heterodimeric nuclease designs, enhance specificity and minimize off-target effects.
- This breakthrough creates isogenic cell models for studying how mutation loads influence disease severity and progression, addressing longstanding research challenges.
- The mpTALEN system shows promise for therapeutic applications, with researchers exploring its adaptation to other mtDNA mutations and in vivo delivery methods.