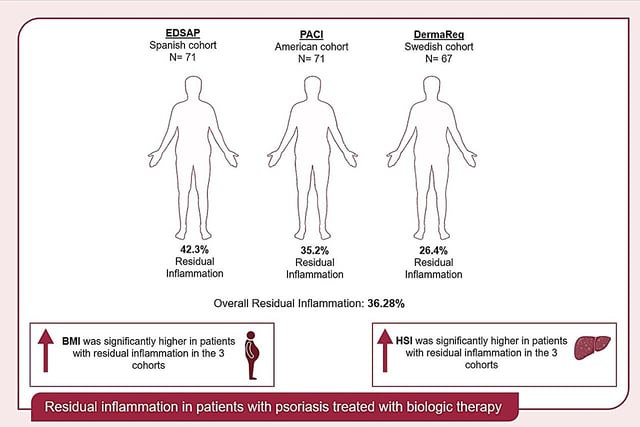
Overview
- A multinational study reveals that 36.3% of psoriasis patients treated with biologics exhibit residual systemic inflammation despite improved skin symptoms.
- Residual inflammation is strongly associated with obesity, increased adiposity, and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).
- Researchers emphasize the need for integrated care approaches addressing systemic inflammation, cardiovascular risks, and metabolic dysfunction in psoriasis patients.
- Advanced imaging and biomarker analysis were used to identify lingering inflammation in 209 patients across Spain, the U.S., and Sweden.
- Experts call for further research to validate these findings and develop comprehensive treatment strategies targeting both skin and systemic health.