Overview
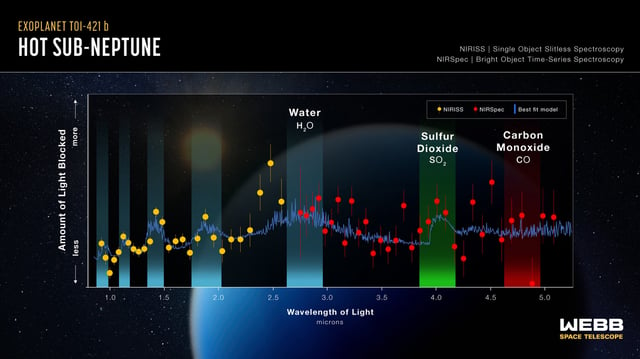
- TOI-421 b, a hot sub-Neptune 245 light-years away, was found to have a clear, hydrogen-dominated atmosphere with water vapor and possible sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- The absence of methane and carbon dioxide supports the theory that high temperatures prevent haze formation by destroying methane before photochemical reactions can occur.
- TOI-421 b’s lightweight atmosphere, resembling its host star’s composition, contrasts with the heavier-molecule atmospheres observed on cooler sub-Neptunes studied previously.
- The planet orbits a Sun-like star, unlike most sub-Neptunes that typically circle cooler red dwarf stars, adding to its distinctiveness.
- Researchers plan further studies of hot sub-Neptunes to determine if TOI-421 b represents a broader class or is an outlier in its atmospheric properties.